Insights GraphQL API
Welcome to Ava Protocol Insights, where we unleash the full potential of dApp developers building on top of Ava Protocol's automation infrastructure. We are thrilled to introduce our GraphQL Data API, a cutting-edge data solution designed to address the limitations and challenges faced by developers. This revolutionary product offers a comprehensive GraphQL Data API that streamlines interactions with the Ava Protocol blockchain, empowering developers and dramatically reducing the development costs associated with dApp creation.
To gain a deeper understanding of the capabilities and data formats of the GraphQL Data API, explore the examples provided below.
The GraphQL Data API harnesses the power of the open-source Subquery project to provide a custom, self-maintained data service. You can find our project's GitHub repository at https://github.com/AvaProtocol/oak-subql
Use Cases#
Simplified Task Tracking: The GraphQL Data API simplifies the tracking and display of user task statuses, eliminating the need for developers to comprehend the intricacies of Ava Protocol's block structure. For example, interpreting a Swap smart contract call with multiple hops on Etherscan can be challenging. Our goal is to alleviate this burden, enabling developers to iterate faster and focus on building their dApps instead of reinventing the wheel.
Real-Time Task Notifications: Another powerful use case for the GraphQL Data API is the seamless integration of pub/sub functionality for task notifications. By allowing users to connect their email or Telegram accounts to our dApp, they will receive real-time notifications when their registered tasks trigger on-chain. This feature enhances user engagement and ensures timely interactions with the Ava Protocol ecosystem.
At Ava Protocol, we are committed to providing developers with the tools they need to unlock the full potential of blockchain automation. Join us on this exciting journey with Ava Protocol Insights and experience a new level of development ease and efficiency.
Working with Ava Protocol Insights GraphQL API#
With GraphQL, you can utilize it to request the precise data you need, thus reducing the number of requests required.
GraphQL data is organized into types, allowing you to employ any client-side GraphQL libraries for API consumption and eliminating the need for manual parsing the data response.
Check out the data models to learn how to explore and discover data models.
API Endpoint#
Our GraphQL API endpoint is at: https://graphql.turing.api.oak.tech.
If you're testing on Turing Staging, use this endpoint https://graphql.turing-staging.api.oak.tech.
GraphiQL Playground#
The playground can be used to interactively explore our data and build queries.
- Turing: turing.explorer.oak.tech
- Turing Staging: turing-staging.explorer.oak.tech
Models#
In GraphQL, data is retrieved by knowing the model name and the relationships between them. For each model, there are specific filters that can be used to fetch only the data needed. For example, finding the balance of a specified wallet.
The best way to discover these models and their filters is through GraphiQL. Click on "SCHEMA" to activate it.
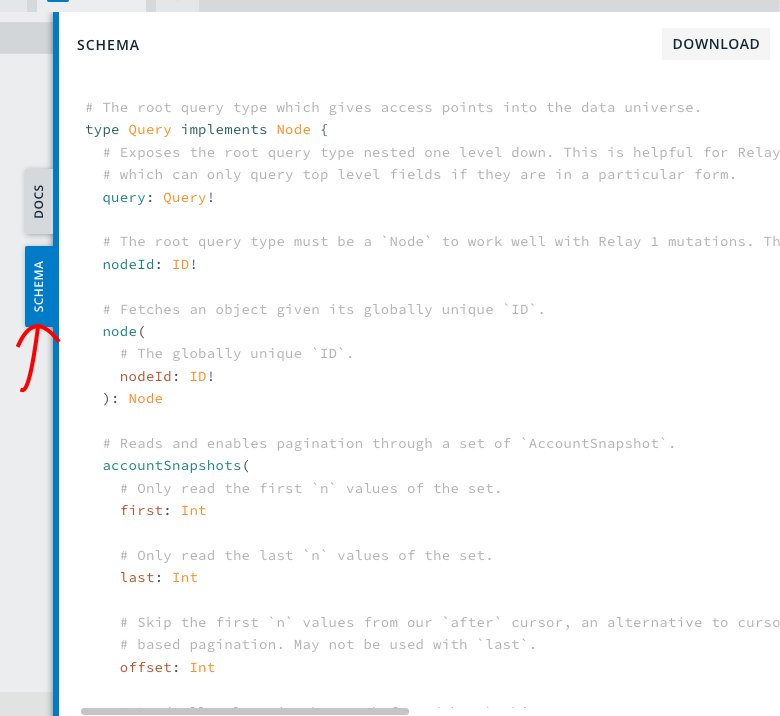
For each model in schema, you will know 3 things: what fields a model have, what filters the model support and how to sort the data.
What fields are included in the model#
Exploring a model let you know what data we offer. For example, when we look into the Event models, we can observe the following fields.

We notice that an event has a field called taskEvents with a type of TaskEventsConnection. By continuing along this path, you will discover all the information you need.
How to filter data#
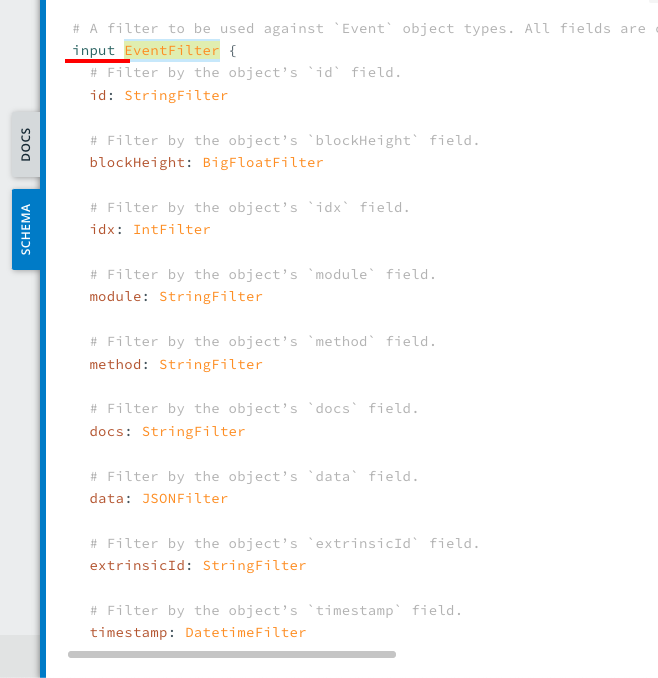
In the model definition, we look at the filter field and its type.
First, we examine the model definition to find the filter type.

Now, we know the type is EventFilter. We can search for it:
How to sort the data#
Similar to the Filter field, we now look at orderBy. To determine the input type for a given model, locate the orderBy field.

Now we can explore the contents of this input type by searching for its name. We will find the following:

When using the GraphiQL playground, this information will be auto-suggested as you type, which helps make writing queries easier.
Authentication#
The API is public, and currently, no authentication is required. Our GraphQL implementation has enabled CORS, allowing any dApps to query directly from any origin.
Fetch Data through the API#
You can use any GraphQL Client, below is an example with Apollo Client, a very popular library.
Query data with Apollo client#
With Apollo Client, we can make query as below:
import { ApolloClient, InMemoryCache, ApolloProvider, gql } from '@apollo/client';
// create a client point to Ava Protocol API
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: ' https://graphql.turing.api.oak.tech',
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
});
// Now we make query
client
.query({
query: gql`
query last_blocks {
blocks(
first: 5,
orderBy: [HEIGHT_DESC],
) {
nodes {
height
hash
weight
timestamp
}
}
}
`,
})
.then((result) => console.log(result));
Query data with Fetch API#
If you don't want to bring extra dependencies of a GraphQL client, you can use traditional browser build-in Fetch API. It's just a normal HTTP POST request to the API.
fetch('https://graphql.turing.api.oak.tech', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
query: `
query my_tasks($account: String) {
tasks(
filter: {
creatorId: { equalTo: $account},
},
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC,]
) {
nodes {
id
timestamp
extrinsic {
method
args
}
}
}
}
`,
variables: {
account: "66vQwvwgH7L23ZxBBFE1DNPadtYqC7iEquq1pEgjtMuVRs74",
},
}),
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((result) => console.log(result));
Query data with curl#
Similar to Fetch API, if you're working in a server side app, you can send request directly without any dependencies.
Sample query to fetch the last 5 blocks of the network.
curl 'https://graphql.turing.api.oak.tech/' \
-H 'Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
--data-binary '{"query":"query last_blocks {\n blocks(\n first: 5,\n orderBy: [HEIGHT_DESC],\n ) {\n nodes {\n height\n hash\n weight\n timestamp\n }\n }\n}"}'
Sorting and pagination#
We strongly recommend setting an ordering for your data. All our endpoints support the orderBy parameter, which allows you to order by one or many fields on the model. Here's an example:
query block {
blocks(
first: 5,
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC, ID_DESC],
) {
pageInfo {
endCursor
}
nodes {
id
height
hash
weight
timestamp
}
}
}
To paginate and load more data, you can take the pageInfo.endCursor from the previous query and pass it as the after parameter in your subsequent query.
query block {
blocks(
first: 5,
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC, ID_DESC],
after:"WyJ0aW1lc3RhbXBfZGVzYyIsImlkX2Rlc2MiLFsiMjAyMy0wNS0zMFQwMTo0NzoyNC4zNDIiLCIxODg1OTg4IiwiMGJiNjEwZTAtNTk3OC00MzY5LWEzMDAtNWQ2NjVmMGY5ZjliIl1d"
) {
nodes {
id
height
hash
weight
timestamp
}
}
}
Popular Queries#
By using our playground, you can explorer the data schema and built-in GraphQL doc generate from the model definition. Below is a list of common queries that you can use to perform common tasks.
Once you're sastified with a query and its result, take it and query it from the app. You can also use variables to make query more flexible.
Get running tasks of a given account#
query my_task {
tasks(
first: 5,
filter: {
creatorId: {equalTo: "66XLkTfzahqCXBoXp38oGJqELTvpvha8BcVLUpNj5mMLoZPQ" }
},
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC]
) {
nodes {
creatorId
timestamp
extrinsic {
method
args
}
}
}
}
Status of task execution of a given account in the past day/week/month#
query my_task_events {
taskEvents(
first: 5,
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC],
filter: {
timestamp: {
greaterThan:"2023-05-30T00:00:0",
lessThan:"2023-05-31T00:00:0"
},
task: {
creatorId: { equalTo:"66XLkTfzahqCXBoXp38oGJqELTvpvha8BcVLUpNj5mMLoZPQ"}
}
}
){
nodes {
module
method
taskId
timestamp
event {
data
}
}
}
}
Search a specific event within a time range#
query my_events {
events(
first: 5,
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC],
filter: {
method : { equalTo: "SuccesfullyAutoCompoundedDelegatorStake"}
timestamp: {
greaterThan:"2023-05-30T00:00:0",
lessThan:"2023-05-31T00:00:0"
}
}
){
nodes {
module
method
data
timestamp
}
}
}
If you are only interested in events specific to running tasks, it is preferred to use task_events as it significantly speeds up the query.
query my_task_events {
taskEvents(
first: 5,
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC],
filter: {
method : { equalTo: "SuccesfullyAutoCompoundedDelegatorStake"}
}
){
nodes {
module
method
event {
data
}
taskId
}
}
}
query my_events {
events(
first: 5,
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC],
filter: {
method : { equalTo: "SuccesfullyAutoCompoundedDelegatorStake"}
}
){
nodes {
module
method
data
}
}
}
Other queries#
Get task history of a given account#
Return a list of tasks, each task node contains a list of event associated with the task itself
query task_history {
tasks(
first: 20,
filter: {
creatorId: { equalTo:"66XLkTfzahqCXBoXp38oGJqELTvpvha8BcVLUpNj5mMLoZPQ"},
},
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC,]
) {
nodes {
id
timestamp
extrinsic {
method
args
}
# fetch events related to this task
taskEvents(first: 10, orderBy:[TIMESTAMP_DESC]) {
nodes {
event {
method
docs
data
}
}
}
}
}
}
Get all events by extrinsic tx hash#
Retrieve all events associated with a specific extrinsic using its hash.
query event_by_tx {
events(
filter: {
extrinsic: {
txHash: {equalTo:"0xebf8b2d614877032cb5e80549c2b673da095283258a5f965740330419fd54f0d" }
}
},
orderBy: [TIMESTAMP_DESC,]
) {
nodes {
id
module
method
data
docs
}
}
}
Get balance snapshot of an wallet at or right before a certain block#
{
accountSnapshots(
first: 10,
filter:{
snapshotAtBlock: {
greaterThan: "1500000",
},
accountId:{
equalTo: "66MGxr9zcyJ6ka6FBQmT1VSvMqARKfwBT7589Fikii1Ci5sg"
}
},
orderBy: [SNAPSHOT_AT_BLOCK_DESC]
) {
nodes {
snapshotAtBlock
accountId
totalBalance
}
}
}