Collator Overview
Pre-requisites to start producing blocks#
Before you start producing blocks and earning rewards as a collator, you must first setup your node. Head over to the following pages for a tutorial on the node setup:
If you have any questions or run into issues, head over to the Ava Protocol Discord for help.
Network Specific Information#
Turing Network - Kusama Parachain#
- PolkadotJS Extrinsics - use this to execute post calls or functions (e.g. signing up to be a collator)
- Subscan - use this for an indexing or reference service with a delightful user experience
- Chain State - use this to query fungible storage items (e.g. the number of selected candidates)
- Chain Constants - use this to query constants for the blockchain (e.g. any parameter with a
constbelow) - Turing Network Telemetry
| Field | Current Value |
|---|---|
Minimum Collator Bond parachainStaking.minCandidateStk | 1 million TUR or 10000000000000000 planck |
Number of selected candidates parachainStaking.totalSelected | 26 |
Round Length parachainStaking.round | 600 blocks or ~2 hours |
Leave candidacy duration parachainStaking.leaveCandidatesDelay | 24 rounds or ~48 hours |
Reduction of self-delegation bond duration parachainStaking.revokeDelegationDelay | 24 rounds or ~48 hours |
Rewards payout parachainStaking.rewardPaymentDelay | Time left to complete current round + 2 rounds or ~4 hours |
Inflation parachainStaking.inflationConfig | 5.00% annually |
Note: The source of truth for the values above is the chain state and constants, so please query that to double-check the values
Helpful query to get the chain state#
You need to query the chain state a number of times for these operations. With that, we've provided a helpful script for you to use. Navigate to the Developer > Javascript tab on the PolkadotJS App.
// Useful to know the duration of different actions from the table above
const minCandidateStk = await api.consts.parachainStaking.minCandidateStk;
const totalSelected = await api.query.parachainStaking.totalSelected();
const roundLength = await api.query.parachainStaking.round();
const leaveCandidatesDelay = await api.consts.parachainStaking.leaveCandidatesDelay;
const revokeDelegationDelay = await api.consts.parachainStaking.revokeDelegationDelay;
const rewardPaymentDelay = await api.consts.parachainStaking.rewardPaymentDelay;
const inflation = await api.query.parachainStaking.inflationConfig();
console.log(`------ HELPFUL CHAIN STATE DATA ------`);
console.log(`Minimum Collator Bond: ${minCandidateStk}`);
console.log(`Number of selected candidates: ${totalSelected}`);
console.log(`Round Length: ${roundLength}`);
console.log(`Leave candidacy duration: ${leaveCandidatesDelay}`);
console.log(`Reduction of self-delegation bond duration: ${revokeDelegationDelay}`);
console.log(`Rewards payout: ${rewardPaymentDelay}`);
console.log(`Inflation: ${inflation}`);
// Useful for collator extrinsics below
const collatorWalletAddress = "YOUR_COLLATOR_WALLET_ADDRESS";
const candidatePool = await api.query.parachainStaking.candidatePool();
const candidateCount = candidatePool.length;
const candidateInfo = await api.query.parachainStaking.candidateInfo(collatorWalletAddress);
const delegationCount = JSON.parse(candidateInfo).delegationCount;
console.log(`------ HELPFUL COLLATOR ACTIONS DATA ------`);
console.log(`Total Candidates in pool: ${candidateCount}`);
console.log(`Your Delegation Count: ${delegationCount}`);
How to register as a collator#
Step 1: Get your session keys#
If you have gone through Step 5 of Using our partner services, you can skip all of Step 1, and proceed to Step 2. You will use that same session key for registration, so keep it handy.
Option 1: Run a CLI command to grab your session keys
If you are on a remote server, it is easier to run this command on the same machine (while the node is running with the default HTTP RPC port configured):
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"id":1, "jsonrpc":"2.0", "method": "author_rotateKeys", "params":[]}' http://localhost:9933
The output will have a hex-encoded "result" field like 0xfoo123bar. The result is the concatenation of the four public keys. Save this result for a later step.
Option 2: Use the PolkadotJS App
Navigate to our other documentation to use the PolkadotJS app to rotate keys. Navigate Step 5 of of Using our partner services. You'll need to have an open websocket to your node to be able to execute this via PolkadotJS UI.
Step 2: Set your session keys#
Step 2.1: Head over to the Developer -> Chain state tab in PolkadotJS
Once you're in the extrinsics tab find session.setKeys.
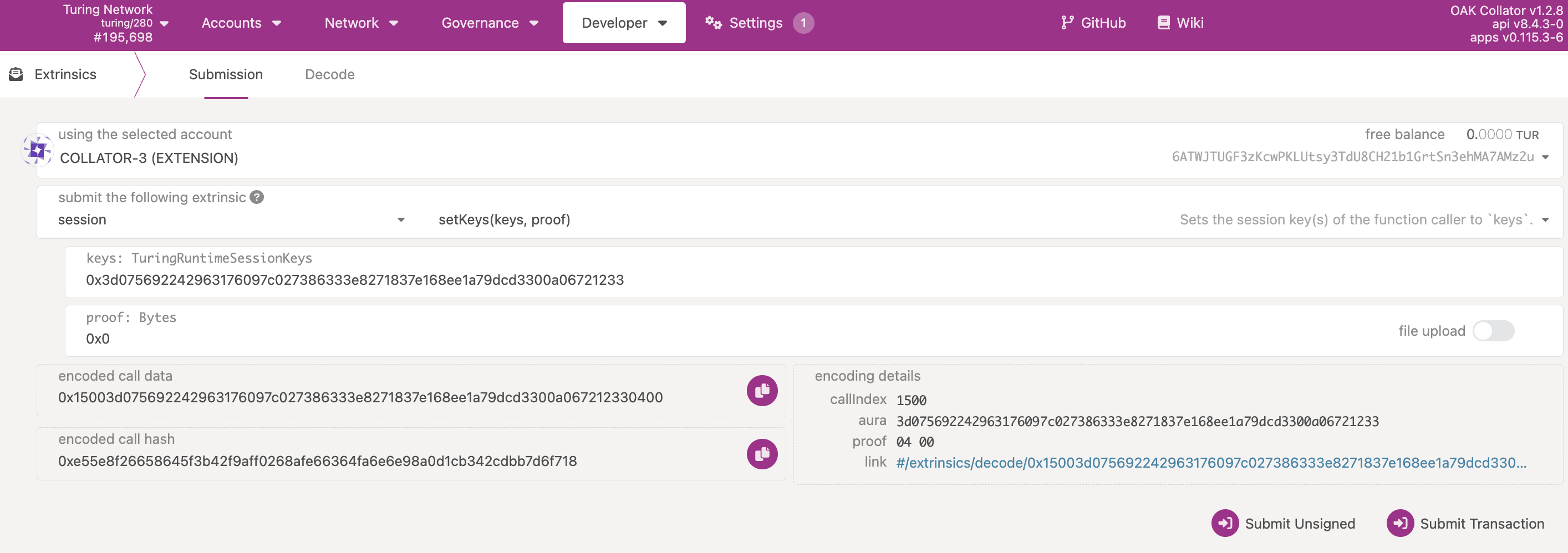
Step 2.2: Set your session keys
Take the result from Step 1.1, in our example 0xfoo123bar, input the following fields:
- wallet: Choose the wallet you intend to use to join as a candidate. In other words, the wallet that has your collator bond ready.
- keys:
0xfoo123bar - proof:
0x0
Step 3: Figure out the size of the candidate set#
As part of a later call, you will need to know how large the current candidate pool is. To compute that, you'll need to navigate to the Storage tab under Developer -> Chain state, and call parachainStaking.candidatePool. This is returned as an array, you'll need to count the number of candidates.
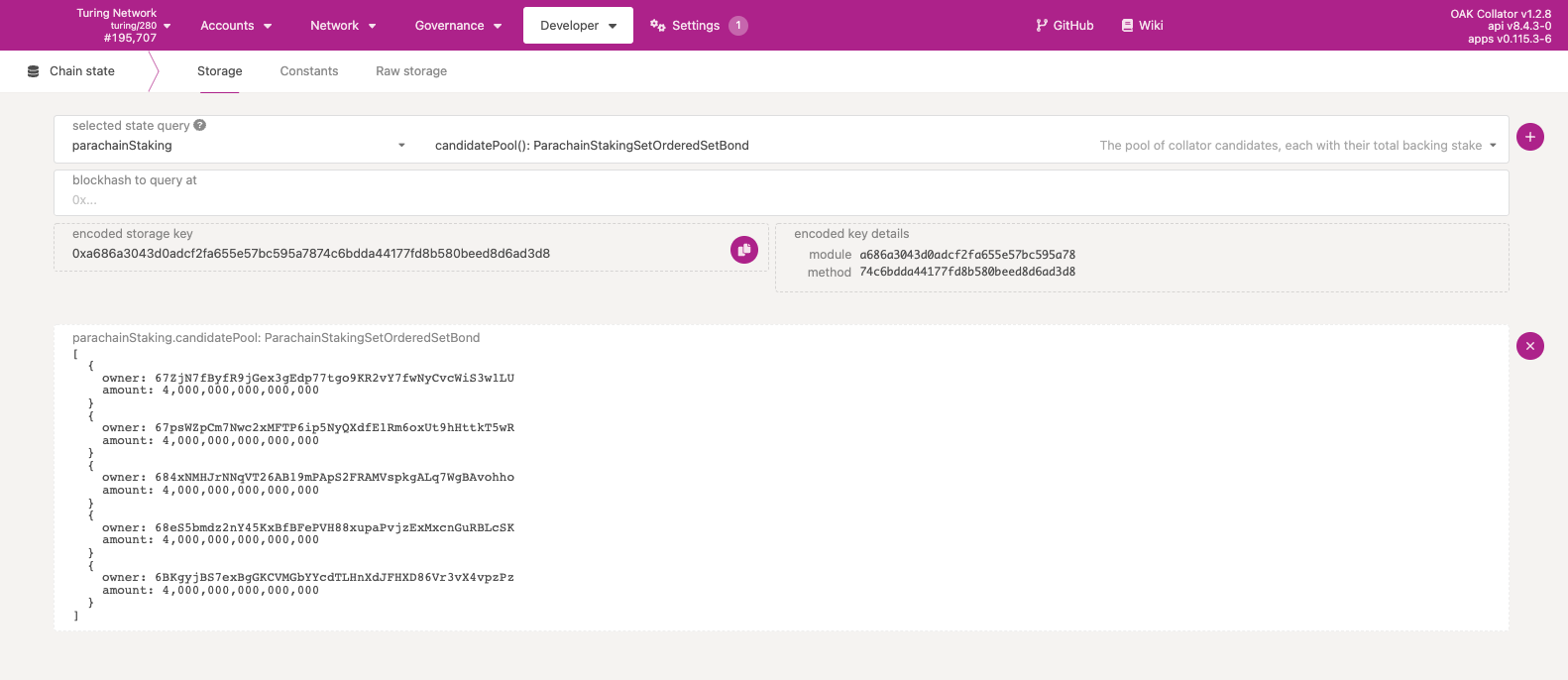
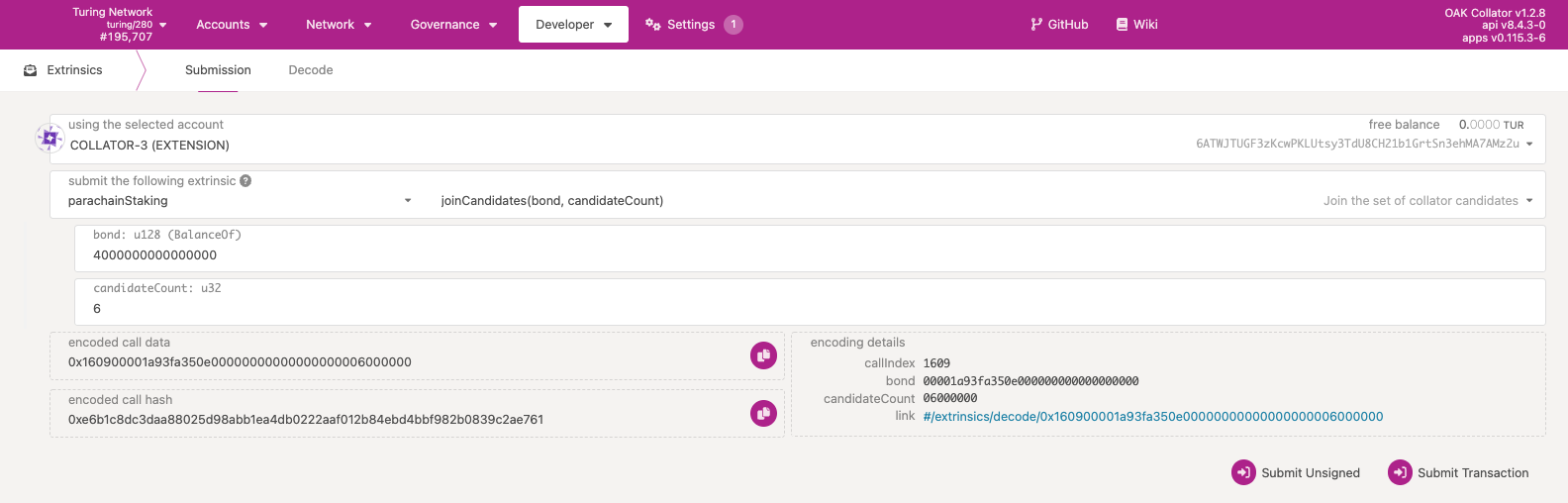
Step 4: Join the candidate set#
In the Developer -> Extrinsics tab, navigate to parachainStaking.joinCandidates.
Once you've set your session keys, use the same wallet from Step 2.2 to signup as a candidate. Make sure you have enough tokens for the bond amount, fees and existential deposit left over.
- wallet: the same wallet you registered your session keys with from Step 2.2
- bond:
10000000000000000(the minimum bond, currently 1M TUR, defined inparachainStaking.minCandidateStk; you can certainly bond more if you wish) - candidateCount:
6(take the number from Step 2 and increment by 1; so from the example above 5+1 = 6)
If the wallet selected doesn’t have more tokens than the minimum bond + a little transaction fee, the extrinsic call will fail and your wallet will not be added to the candidate pool.
Step 4: Confirm your candidacy#
Similar to Step 3, you'll have to navigate to the chain state page, and call parachainStaking.candidatePool and search for your wallet address in the array returned.
Step 5: Wait#
Top delegated collators will be part of the active set, which is set / chosen at the beginning of each round.
Step 6 (Optional, but recommended): Setup your on-chain identity#
To increase your chances of community members staking to your collator, we recommend you setup an on-chain identity.
How to leave as a collator#
There are two ways to leave as a collator.
Option 1: Short-term leave#
If you need to run node upgrades and other maintenance operations, you can navigate to the extrinsics page and call parachainStaking.goOffline. This allows you to leave as a candidate without unbonding. You can return by calling parachainStaking.goOnline.
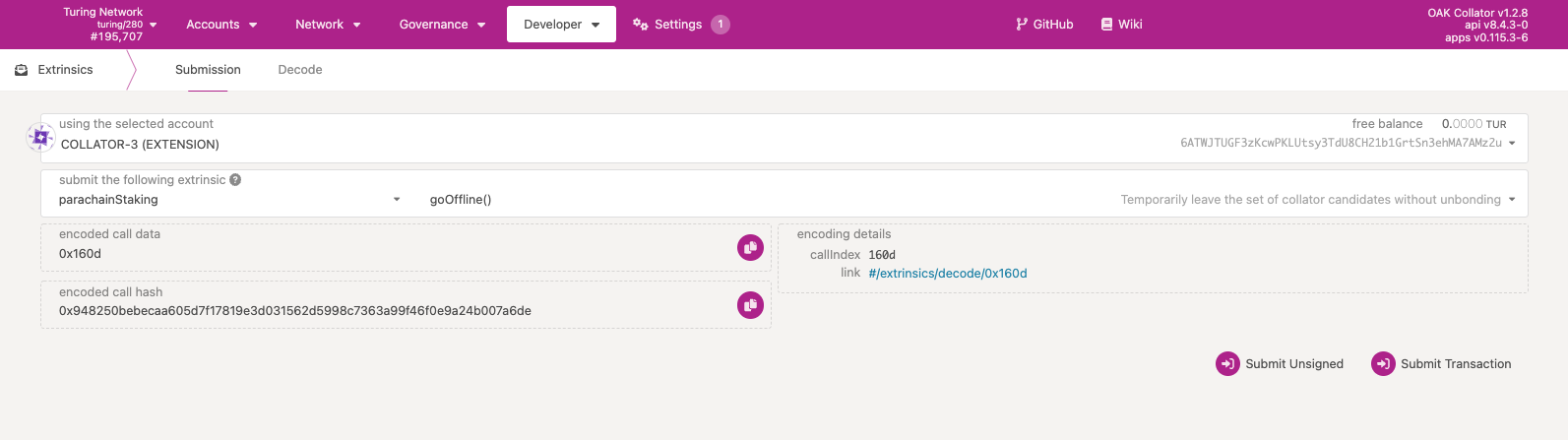
Option 2: Long-term leave#
If you need to leave the candidate set and unbond, you have to perform two calls.
Step 1
Navigate to the extrinsics tab, and go to parachainStaking.scheduleLeaveCandidates with the candidateCount re-computed from Step 3 above. Note that the candidateCount may have increased or decreased since you last did Step 3.
If the call succeeds, you are removed from the pool of candidates so you cannot be selected for future collator sets, but you are not unbonded until their exit request (Call #2) is executed. Please note that this is not an instant execution, you'll need to wait which is the next step.
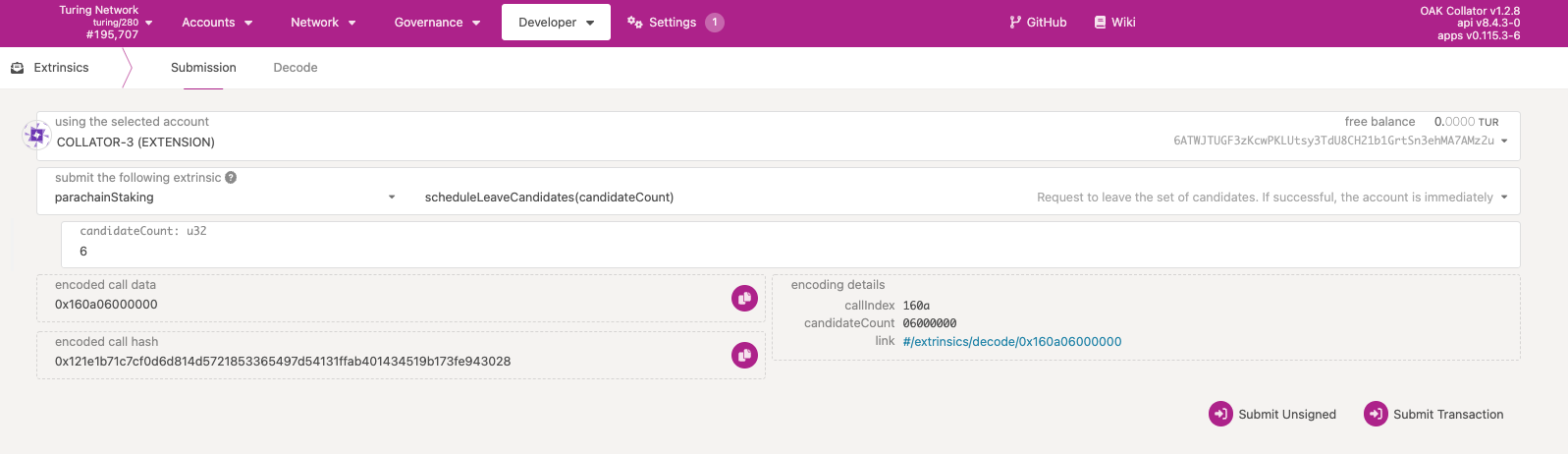
Step 2 Wait for however long Leave candidacy duration is from the table above. After that time has passed, then you can proceed to the next step.
Step 3
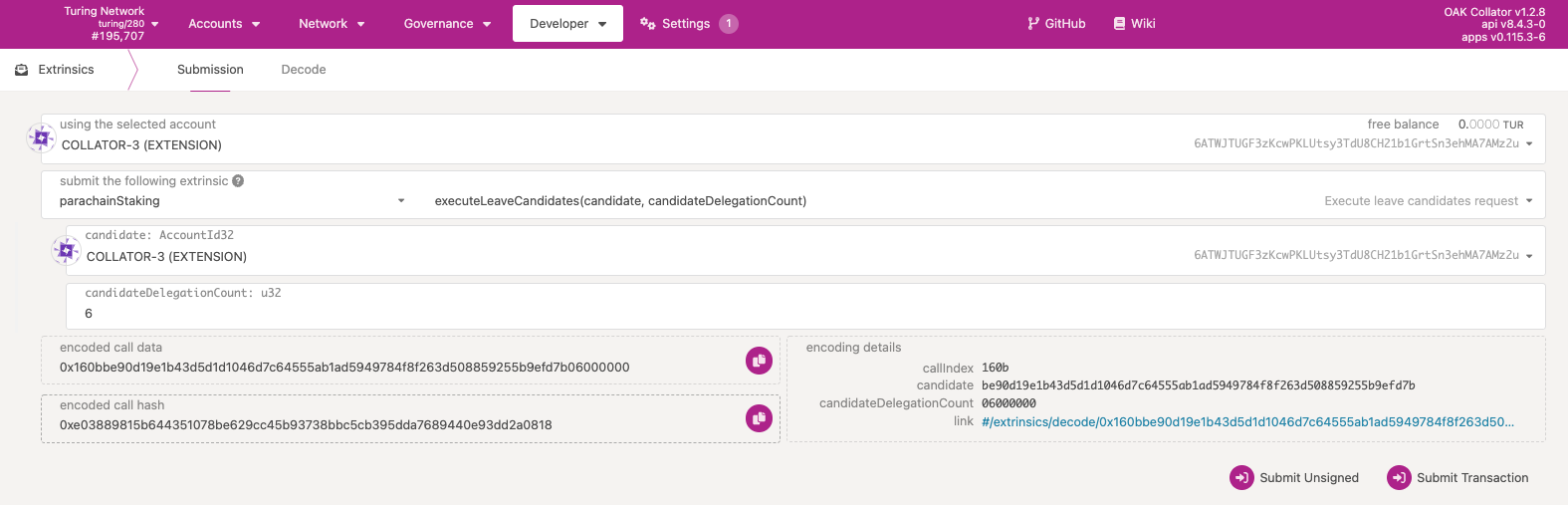
Query for the number of delegates for your collator by going to the Chain State tab and executing parachainStaking.candidateInfo. From this output, grab the delegationCount and use that as your number of delegates.
Step 4
Navigate to the extrinsics tab, and go to parachainStaking.executeLeaveCandidates with the delegationCount from Step 3 above.
FAQ#
For any questions or support, please reach out via Ava Protocol Discord, or email <collators@avaprotocol.org>.
When will my collator start producing blocks?#
Collators start producing blocks 2 rounds after they become the parachainStaking.selectedCandidates.
For example, in Turing, if you've joined as a collator candidate, and you are considered as one of the top delegated collators, you can call parachainStaking.round in the chain state, you will see the following output.
{
current: 88
first: 200,737
length: 600
}
Because you opted to join sometime during this round, you can calculate the FIRST_BLOCK_NUMBER_OF_ROUND + 1800, which would mean you can expect to start producing blocks at 202,537.
When will my new session keys be used?#
New session keys are used after the current session completes and two full sessions elapse.
Under what circumstances would I be removed from the candidate pool?#
Currently slashing has not been implemented on the Turing network. You will only be removed from the candidate pool if you initiate leaving the pool through extrinsic.
I want to run multiple collators, can I use the same wallet?#
No. Each collator must be associated with a unique wallet in order to join the candidate pool.
What rewards will I get?#
Collators collect 2 types of rewards: the collator reward and the staking reward. 1% annual inflation goes directly to collators. This does not dilute based on the number of people staking to your node. 2.5% annual inflation goes to staking rewards. This is split proportionately among all stakers to that node. This will be diluted as more people stake to your node. This creates an incentive for roughly all the nodes to have similar stakes for stakers to maximize their APY.
Performance differences between nodes may cause stakers to choose to split their stakes in way that is not perfectly even. Since rewards are paid out per block successfully authored. For more information, please read our Turing Tokenomics Paper.
If I joined as a collator in the candidate pool, and the minimum self bond increases, what happens to my node?#
Collators in the candidate pool with the minimum self-bond met will remain as valid collators in the candidate pool. The raised minimum self bond will not prevent that collator from entering the active set given the total amount staked to that collator is high enough to enter the active set. They will be grandfathered in at the previous self-bond.
If you choose to leave the candidate pool, you will be subject to the higher minimum bond when re-entering.